mount point does not exist что делать
Самые часто возникающие ошибки при монтировании папки в Linux
Начинающие пользователи Linux систем сталкиваются с кучей различных ошибок. Которые в свою очередь возникают по самым нелепым причинам. Пользователь не дописал команду, сделал синтаксическую ошибку и т.д. Например, когда неопытный пользователь пытается смонтировать сетевую папку с помощью команды mount, появляются ошибки типа can’t find in /etc/fstab или mount does not exist. Сегодня рассмотрим самые часто возникающие ошибки при подключение сетевой папки в Linux.
Рекомендую прочитать следующие статьи из которых вы узнаете как подключить сетевую папку в различных Linux системах.
Ошибка при монтировании папки can’t find in /etc/fstab
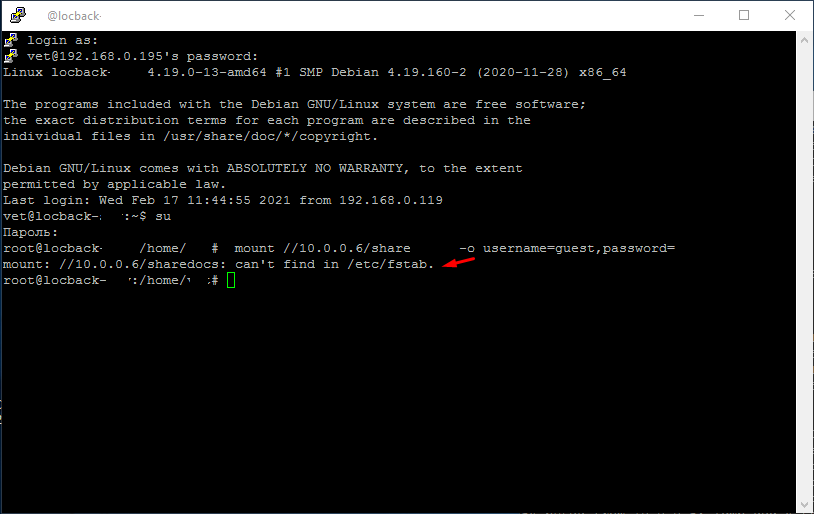
И так вы вводите команду монтирования сетевой папки и видите сообщение can’t find in /etc/fstab. Это говорит о том что вы не указали папку куда будет смонтирован сетевой диск. Т.е вы ввели следующею команду.
/10.0.0.6/share — указали где располагается сетевая папка
username=guest — указали пользователя
password= — без пароля
Правильная команда должна выглядеть так.
/mnt/share/ — забыли указать место куда будет смотриван сетевой ресурс
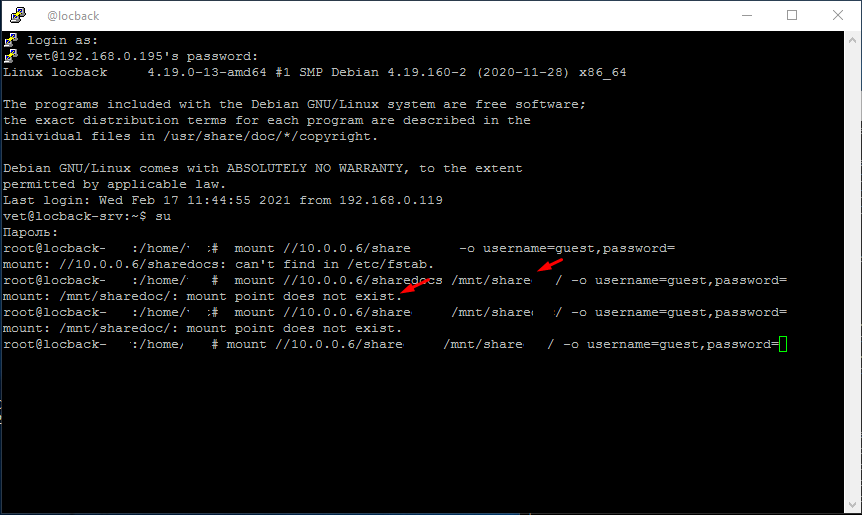
Ошибка mount does not exist
Дальше после ввода правильной команды для монтирования сетевой папки вы можете увидеть сообщение mount does not exist. Этого говорит о том что папки share указанной в строчке /mnt/share/ нет.
Это особенность подключения сетевой папки в Linux. Вы должны сами создать пупку /mnt/share/ к которой будет монтироваться сетевой диск.
Если папка создана, команда введена правильно без ошибок то сетевой диск должен подключиться без каких либо проблем.
Проверяйте правильность ввода команда и указания путей это две самые главные проблемы начинающих пользователей Linux.
Создание точки монтирования, если она не существует
При использовании mount утилиты, если вы указали несуществующий каталог, это считается ошибкой. Есть ли какая-либо опция, которую я могу использовать, чтобы точки монтирования создавались автоматически, если они еще не существуют?
если вы хотите создать точку монтирования с именем DISK1, введите в терминале следующую команду:
Нет, утилита для простого монтирования не предлагает такой опции.
Это делается при монтировании из файлового менеджера, такого как Nautilus.
Установите утилиту pmount и дайте ей автоматически обрабатывать точки / media / user / mount. Больше не нужно беспокоиться о том, как и где / media / user / devices монтируются и под какими именами.
Затем, когда вы вставляете съемное устройство, оно автоматически монтируется в / media / username / по имени.
Например: моя флешка называется «SYSBKP», поэтому она автоматически монтируется как /media/pi/SYSBKP
Он также обрабатывает неожиданные выбросы. И перемонтирует. Молча.
За кулисами это гарантирует, что буферы всегда очищаются на случай, если USB извлечен без предупреждения. Больше не нужно синхронизировать, синхронизировать, синхронизировать, как в старые времена.
Это означает, что вы не можете писать сценарии, которые принимают имя точки монтирования (если вы не включите в скрипт все команды монтирования). Если вы выберете неправильный, он будет рассматриваться как локальный каталог.
pmount гарантирует, что ваш USB-накопитель имеет собственную назначенную точку монтирования в / media / username /. В этом случае это всегда / media / pi / SYSBKP
Это также работает, когда вы вставляете другую флешку с тем же именем. Так что не по UUID.
Я использую это не только для флэш-накопителей, но и для полноразмерных резервных накопителей, для резервных копий rsync и полностью уверен, что сценарии будут работать без изменений.
Это простое, надежное решение для создания точек монтирования.
Обратите внимание, что я лично протестировал его с NTFS, FAT32 и различными дисками в формате EXT. Если диск содержит несколько разделов, он будет монтировать обычные файловые системы индивидуально по имени, избегая раздела подкачки. Это все видно в nautilus и более подробно упоминается в этом разделе вопросов и ответов:
Я вижу в комментариях проблему с дисками NFS + Time Machine.
Это может или не может работать автоматически
Creating a mount point if it does not exist
When using the mount utility, if you specify a directory that does not exist, that is considered an error. Is there any option I can use so that mount points get automatically created if they don’t already exist?
3 Answers 3
if you want to create a Mount Point called DISK1, then type the following command in the terminal :
No, the bare mount utility do not offer such an option.
It is done when mounting from a file manager like Nautilus, though.
Install the pmount utility and let it handle /media/user/ mount points automatically. No more worries about how and where /media/user/ devices mount and by which names.
Then whenever you insert a removable device, it will automatically be mounted under /media/username/, by name.
For example: My USB stick is named «SYSBKP» so it automatically mounts as /media/pi/SYSBKP
It also handles unexpected ejects. And remounts. Silently.
Behind the scenes it makes sure the buffers are always flushed just in case the USB is pulled without warning. No more need for sync;sync;sync like the old days.
In any case, pmount is a very important piece of software to have if you use /media/username/ for removable devices.
If you don’t use it, the default action is to create new mount points for each insertion, with a digit appended to the name for each one. Even normal ejects cause this behavior. You end up with mount points like /media/username/SYSBKP, /media/username/SYSBKP1, /media/username/SYSBKP2, etc.- and you don’t know which one is the active one.
This means you can’t write scripts that assume the mount point name (unless you include all the mount commands in the script). Should you choose the wrong one it is treated as a local directory.
pmount makes sure your USB drive it has its own assigned mount point under /media/username/. In this case, it is always /media/pi/SYSBKP
It also works when you put in another USB flash drive with the same name. So it is not going by UUID.
I not only use this for flash drives, but also for fulll-size powered backup drives, for rsync backups, and have full confidence that the scripts will work without modification.
It is a simple, reliable solution to creating mount points.
Note that I have personally tested it with NTFS, FAT32 and the various EXT formatted drives. If the drive contains multiple partitions it will mount regular file systems individually by name, avoiding the swap partition. This is all visible in nautilus, and is alluded to in more detail in this Q&A:
I see in comments there is an issue with the NFS+ Time Machine drives.
It may or may not work automatically
It turns out Apple does a couple slick things with the file system to make incremental backups work, including hard linking to directories, which isn’t allowed in Linux. So for anyone that needs to access their Time Machine from something other than its associated Mac, here’s how you do it. (see linked article for the rest)
Arch Linux
You are not logged in.
#1 2012-02-12 04:18:24
[closed] chroot questions, mount point proc/ does not exist [restored]
recently I experienced what seems to be a moderately frequent issue: I updated my kernel and on next boot got the error about ERROR: unable to determine major/minor number of root device
found that the best way to fix this is to chroot to my existing arch system using another linux cd (I chose to simply use Arch live boot because I have the ISO sitting on my desktop) and then downgrade the kernel to previously good/known working version.
So that is what I am working on and I have this wiki page (https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Change_Root) about change root that is a good guide.
Here is my quesiton
1.) I booted arch live from iso
2.) mkdir for /mnt/arch
3.) mount /dev/ /mnt/arch
I mounted my /dev/sda1 because that is what the boot star is next too (presumably that means its where the system kernel is? I am a little shaky on this)
and get that mount point proc/ does not exist. I make an ls and sure enough there is no proc/ (I am wondering maybe if I mounted the wrong device??
Can someone provide advice as to whether I mounted the correct device from that screen shot and/or if the proc/ folder is missing what does that mean?
Sorry but the chroot wiki is either not informative enough or I am just too new.
Last edited by sotu (2012-02-12 19:25:11)
mount point does not exist #112
Comments
chornlgscout commented May 13, 2020
openebs-zfs-node openebs-zfs-plugin says:
csi/pvc-b3f312c4-0f1d-4348-8196-dcb19bec206c/mount: mount point does not exist.
E0513 15:35:14.497336 1 mount_linux.go:147] Mount failed: exit status 32
Environment:
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
chornlgscout commented May 13, 2020
Obviously, the openebs-zfs-node openebs-zfs-plugin needs to mount the real kubelet directory at the real path. Modified zfs-operator.yaml with that mount, and all is well.
pawanpraka1 commented May 14, 2020
@chornlgscout, can you describe a little bit about the setup? How you are using the ZFS-LocalPV? Is it a production or dev setup? What features you are using or looking for?
If possible, can you sign the adopters file for us and detail your use-case a bit? It will help us out when working with CNCF. Here is the adopters file where a lot of users have already signed it : openebs/openebs#2719.
chornlgscout commented May 14, 2020
Briefly: Development POC, trying to port a legacy application using local zfs storage behind components including elasticsearch, kafka and zookeeper. We intend to dynamically allocate zvols to these components, to snapshot them on upgrade, and roll them back on rollback. Intent is for this to be a locally hosted production product.
I’d also like to be able to use shared local zvols for communal scratch space (e.g. shunting file based logs to filebeat), but that seems less likely.
pawanpraka1 commented May 14, 2020 •
pawanpraka1 commented May 15, 2020
adding the details from the issue #113
wirwolf commented Aug 18, 2020
Rancher 2.4.5
kubernetus v1.18.3
MountVolume.NewMounter initialization failed for volume «pvc-45421d5d-b8fd-40d0-9918-32eab3547156» : path «/var/openebs/local/pvc-45421d5d-b8fd-40d0-9918-32eab3547156» does not exist
pawanpraka1 commented Aug 18, 2020 •
@wirwolf which storage engine you are using? does not look like you are using localpv zfs? Seems like you are using localpv hostpath storage engine? can you share your storageclass yaml?
quexten commented Dec 9, 2020
I have the same issue. I was doing some unrelated work on the cluster, rebooted and suddenly none of my pods which are using a zfs-localpv volume are starting, with the same error.
I manually created this path after which the pod started fine. But this is obviously not the correct solution.
Reinstalling openebs or destroying and re-creating my zpool did not work.
My storage class:
Other than that I installed it just like in the readme.
pawanpraka1 commented Dec 9, 2020 •
@quexten this looks to be different issue. Can you elaborate a little bit about your cluster, is it on-prem cluster or the cluster is managed by any cloud provider? What is the k8s version you are using? What is the ZFS-LocalPV version?
That directory normally gets created by the kubelet. I need to understand why it did not happen in your case. Also, from your description, it looks like the deployment worked the first time and got the issue after node reboot. This looks strange.
quexten commented Dec 9, 2020
ahlgol commented Dec 13, 2020
Also running ZFS-LocalPV with microk8s on a single node, and after a reboot this weekend the volumes won’t get mounted. Have to create the pvc-. /mount manually. It has been running fine for 12 weeks before this, going through multiple reboots. Maybe its an upgrade microk8s that’s causing trouble?
quexten commented Dec 13, 2020
I’m not using microk8s and still got the issue, so it must be something in general with the updates. Before I got this issue I did run a full system software upgrade. Setting up a new cluster with Kubernetes 1.20.0 lead to the same issue.
ahlgol commented Dec 13, 2020
Could this be relevant? (from k8s 1.20 release notes)
For CSI drivers, kubelet no longer creates the target_path for NodePublishVolume in accordance with the CSI spec. Kubelet also no longer checks if staging and target paths are mounts or corrupted. CSI drivers need to be idempotent and do any necessary mount verification. (#88759, @andyzhangx) [SIG Storage]
pawanpraka1 commented Dec 13, 2020 •
ahlgol commented Dec 14, 2020
@pawanpraka1, Yup, the «mount does not exist» is gone now! 👍 Still getting some verifyMount: device already mounted at that I have to unmount manually from previous pods, and I have some new permission issues on mariadb:10 containers, but it might be unrelated. Will dig deeper tonight. Thanks!
pawanpraka1 commented Dec 14, 2020 •
thanks @ahlgol, There are 3 things here
Got a new issue verifyMount: device already mounted at and you have to unmount manually from previous pods. This is interesting. How did you get into this issue? This should not happen as after reboot the volume will get umounted automatically?
Can you elaborate the steps to reproduce this?
You have permission issues on mariadb. Let me know if you need any help here.
@quexten could you also try out the RC2 yaml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openebs/charts/2c77087c93fd9088984dc6dbe784ff8c6a6c8100/2.4.0/zfs-operator-RC2.yaml and let me know if that is working for you.
ahlgol commented Dec 14, 2020
When I stop/start microk8s or reboot the machine the PVs are already mounted when the pods tries to start (stopping microk8s doesn’t remove the mount). Not sure what mounts if after reboot yet as they obviously aren’t present in fstab. Will investigate further.
Error message in full:
MountVolume.SetUp failed for volume «pvc-5033d122-dcca-466e-88ba-bdb8bd3a8bce» : rpc error: code = Internal desc = rpc error: code = Internal desc = verifyMount: device already mounted at [/host/var/snap/microk8s/common/var/lib/kubelet/pods/b8990882-5093-4786-8341-af58891c3e0e/volumes/kubernetes.io
The pods fail to start after this, even though the volume is actually mounted at the correct mount point.
After a manual unmount, the pods (eventually) start but I still have permission voes. will try to understand them now.
pawanpraka1 commented Dec 15, 2020 •
Not sure what mounts if after reboot yet as they obviously aren’t present in fstab
ahlgol commented Dec 15, 2020
pawanpraka1 commented Dec 15, 2020
ahlgol commented Dec 15, 2020 •
Thanks! Rebooting without issues now. 👍
Not sure what went wrong either, and the mount failures were intermittent, mounting correctly sometimes. The mounts weren’t created when disabling the microk8s service, so it was nothing external. Possibly a timing issue or network issues (the dns runs in microk8s as well, so it wasn’t working) caused a hiccup, which restarted pods and so zfs-plugin tried to mount the volumes twice.
My permission problems seem to stem from the fact that the mounts are now created with a umask of 000. Chmoding it to 100 lets mariadb start. Not sure what microk8s set it to by default before (which worked) but will have to go looking for the best ways to set it to the correct umask in the pod spec I guess. ^_^
pawanpraka1 commented Dec 16, 2020 •
Thanks! Rebooting without issues now.
The mounts weren’t created when disabling the microk8s service, so it was nothing external.
I guess, that is becasue the change in kubernetes 1.20 stopped creating the mount directory and also stopped checking if the volume is already mounted, don’t ask the CSI driver to mount again. There are a lot of CSI drivers which depend on that. This must have broken many CSI drivers.
My permission problems seem to stem from the fact that the mounts are now created with a umask of 000.